Showing posts with label Technical. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Technical. Show all posts
Thursday, November 29, 2018
Checking your site SSL
I have been working on trouble shooting web site's SSL recently and came across some very useful free tools for checking the site's SSL in this case. I think it's worth for me to keep a record here and hopefully it's useful for you too :
Easy to use - SSL Checker from SSLShopper
More Complete Info - SSL Report from Qualys
Tuesday, October 09, 2018
FREE Cryptocurrency API
I have been working on some Cryptocurrency project and looking for some free API to use in my project. This post shall serve as my own record in the path of constructing my project and hopefully someone might find it usefull as well. Following are some of the free API that i found and i only focusing those that are able to support realtime(or almost realtime) date feeding.I will be keep updating the list below as i am constructing my project.


CoinAPI API
- FREE
- Support websocket, which seem to be realtime updating.
- For the api document, it seem to be able to support retrieval of orderbook.
- FREE account have the following limitation :
- only support retrieval of trade details using websocket.
- websocket only limited to 15min daily connection time.
- only support retrieval of trade details using websocket.
- websocket only limited to 15min daily connection time.
CryptoCompare API
- FREE
- Support websocket, which seem to be realtime updating, sample : Trade Info
- unable to locate info to retrieve orderbook details.
Nomic API
- FREE and no rate limits. (yet to find out)
- Mentioned to support websocket, but unable to find details info from the API doc.
Wednesday, August 15, 2018
Running Redmine using Docker
Run into Docker recently and would like to work on something. Let's try on running Redmine using Docker. Following are the steps to get it running in your localhost:
1. Install and get docker running in your PC.
2. Run into command prompt and start doing the real docker job.
3. In the command prompt pull Redmine using the following command:
$ docker pull redmine
4. Once you docker pull redmine successfully, now you can run redmine in a container using the following command:
$ docker run -d -P --name myRedmine redmine-d will detach out terminal
-P will publish all exposed ports to random ports
-name corresponds to a name we want to give5. Now we can see the ports by running the following$ docker port myRedmine 3000/tcp -> 0.0.0.0:32769
6. You can now open http://localhost:32769. You might need to wait a while for redmine to start.7. You can also specify a custom port to which the client will forward connections to the container using the following command :$ docker run -d -p 8080:3000 --name myRedmine redmine
Monday, June 25, 2018
Raspberry PI Zero and Raspberry PI Zero W

I personally prefer Raspberry PI Zero with WIFI as it's easier to get connected to the internet for configuration. To setup the the Pi, you can download the respbian images from the following location :
I shall put on the steps in a separate blog entry later for setting up the PI. So please stay tune with me.
Sunday, November 26, 2017
Running Docker in my OrangePi Lite
Fascinated to mini PC for sometimes already. Only recently have some free time to play around with my long purchased OrangePi Lite. As an alternative for Raspberry Pi, I got my H3 ARM, Cortex-A7 Quad Core, 512mb RAM OrangePi Lite, for less than USD$14. After tried several way which didn't work, i have found the following setup are able to run Docker :
1. download the armbian server image using the following link :
https://www.armbian.com/orange-pi-lite/
2. burn the image using Win32DiskImage into a SD card with minimum 8GB storage
3. Plugin the SD card into the OrangePi Lite slot and start the OrangePi.
4. Following the instruction on the screen to configure your account and finally reboot the device.
5. Run "armbian-config" to configure WIFI connection.
6. Within armbian-config, switch to use to use Dev builds instead of stable build.
7. run apt-update and then apt-upgrade.
8. reboot the device. After reboot, we are ready to setup docker.
9. Use the following steps to setup docker :
i. Install packages to allow
apt to use a repository over HTTPS:$ sudo apt-get install \
apt-transport-https \
ca-certificates \
curl \
software-properties-commonii. Add Docker’s official GPG key:
$ curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
iii. Verify that you now have the key with the fingerprint:
9DC8 5822 9FC7 DD38 854A E2D8 8D81 803C 0EBF CD88,
by searching for the last 8 characters of the fingerprint.
$ sudo apt-key fingerprint 0EBFCD88
pub 4096R/0EBFCD88 2017-02-22
Key fingerprint = 9DC8 5822 9FC7 DD38 854A E2D8 8D81 803C 0EBF CD88
uid Docker Release (CE deb)
sub 4096R/F273FCD8 2017-02-22
iv. Use the following command to set up the stable repository. You always need the stable repository, even if you want to install builds from the edge or test repositories as well. To add the edge or testrepository, add the word
edge or test (or both) after the word stable in the commands below.Note: Thelsb_release -cssub-command below returns the name of your Ubuntu distribution, such asxenial. Sometimes, in a distribution like Linux Mint, you might have to change$(lsb_release -cs)to your parent Ubuntu distribution. For example, if you are usingLinux Mint Rafaela, you could usetrusty.
armhf:
$ sudo add-apt-repository \
"deb [arch=armhf] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
$(lsb_release -cs) \
stable"
v. Install the latest version of Docker CE, or go to the next step to install a specific version. Any existing installation of Docker is replaced.
$ sudo apt-get install docker-c
vi. Verify that Docker CE is installed correctly by running the
hello-world image.$ sudo docker run hello-world
This command downloads a test image and runs it in a container. When the container runs, it prints an informational message and exits.
Monday, November 20, 2017
Raspbian Pi for ORange Pi - Fully expand SD space
Following are the steps to expand the SD space within Raspbian Pi running in My Orange PI :
root@orangepi:~# fdisk /dev/mmcblk0
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/mmcblk0: 15.8 GB, 15804137472 bytes
4 heads, 16 sectors/track, 482304 cylinders, total 30867456 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x34605ba5
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/mmcblk0p1 40960 124927 41984 83 Linux
/dev/mmcblk0p2 124928 7170047 3522560 83 Linux
Command (m for help): d
Partition number (1-4): 2
Command (m for help): n
Partition type:
p primary (1 primary, 0 extended, 3 free)
e extended
Select (default p): p
Partition number (1-4, default 2): 2
First sector (2048-30867455, default 2048): 124928
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (124928-30867455, default 30867455):
Using default value 30867455
Command (m for help): w
Theen quit (command q), reboot. You will then be able to use resize:
resize2fs /dev/root
df -h
root@orangepi:~# fdisk /dev/mmcblk0
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/mmcblk0: 15.8 GB, 15804137472 bytes
4 heads, 16 sectors/track, 482304 cylinders, total 30867456 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x34605ba5
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/mmcblk0p1 40960 124927 41984 83 Linux
/dev/mmcblk0p2 124928 7170047 3522560 83 Linux
Command (m for help): d
Partition number (1-4): 2
Command (m for help): n
Partition type:
p primary (1 primary, 0 extended, 3 free)
e extended
Select (default p): p
Partition number (1-4, default 2): 2
First sector (2048-30867455, default 2048): 124928
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (124928-30867455, default 30867455):
Using default value 30867455
Command (m for help): w
Theen quit (command q), reboot. You will then be able to use resize:
resize2fs /dev/root
df -h
Thursday, March 09, 2017
Resetting User's password in Bitnami Gitlab using command line
Just for my own record or for someone that needed it :
First create a backup of your stack just in case :
After that just run the following to reset the user's password :
First create a backup of your stack just in case :
sudo /opt/bitnami/ctlscript.sh stop
cd /opt
sudo cp -a bitnami bitnami_backup
sudo /opt/bitnami/ctlscript.sh start
After that just run the following to reset the user's password :
cd /opt/bitnami/apps/gitlab/htdocs
echo 'u=User.find_by_id(1); u.username="NEW_USERNAME"; u.save!;' | RAILS_ENV=production /opt/bitnami/ruby/bin/ruby /opt/bitnami/apps/gitlab/htdocs/bin/rails c
echo 'u=User.find_by_id(1); u.password="NEW_PASSWORD"; u.save!;' | RAILS_ENV=production /opt/bitnami/ruby/bin/ruby /opt/bitnami/apps/gitlab/htdocs/bin/rails c
Wednesday, July 06, 2016
Setup gitolite in D-Link DIR-620 router running openwrt

- Setup USB Storage. In this case i am using a 8gb USB thumb drive using the following command (i have formated my usb drive into ext4 format):
opkg install kmod-usb-storage block-mount kmod-fs-ext4
- Setup gitolite in the router using the following step :
- Install necessary components
opkg install git perl perlbase-essential perlbase-getopt perlbase-findbin perlbase-cwd perlbase-config perlbase-file perlbase-data perlbase-bytes perlbase-xsloader openssh-keygen perlbase-hostname perlbase-fcntl perlbase-io perlbase-symbol perlbase-selectsaver perlbase-errno perlbase-base
- Backup authorized_keys file if exist
cp -p /etc/dropbear/authorized_keys /etc/dropbear/authorized_keys_backup
- Create directory under mnt and mount usb drive
mkdir /mnt/usb
mount /dev/[sda2]/mnt/usb
- Move root to usb and create link
cd /
mv root /mnt/usb
ln -s /mnt/usb/root root
- Download gitolite
cd /root
git clone git://github.com/sitaramc/gitolite
- Install a link to gitolite executable into /usr/bin
gitolite/install -ln /usr/bin
- create gitolite logfile directory
mkdir /root/.gitolite mkdir /root/.gitolite/logs
- Copy your ssh public key to root, you may use puttykeygen tools to get the single line public key and paste to a new file via vi command
vi yourname.pub
- Setup gitolite
gitolite setup -pk yourname.pub
- now you can remove the public key file and create a link to /root/.ssh/authorized_keys in /etc/dropbear/authorized_keys
rm yourname.pub
rm /etc/dropbear/authorized_keys ln -s /root/.ssh/authorized_keys /etc/dropbear/authorized_keys
- now you can admistrate your gitolite by cloning the gitolite-admin repo
git clone root@OpenWRTBox:gitolite-admin
Thursday, December 31, 2015
Installing Print Screen feature to my china made pad (Homily WinPad)
just got my new Homily Winpad and figure out it doesn't have google play with it and unable to do a print screen. Therefore, i would like to share on how i add a print screen feature to my China made Homily WinPad.
1. Using the WinPad (Android) browser, download the following file
http://bit.ly/1YV3pM0
2. Install the app accordingly
3. Configure the app so that it start automatically every time you start you WinPad in Android.
4. you can capture any screen from android using the combination following combination keys:
[Power]+[Volume Down] for 2 seconds.
Sample screen captured / print screen. Nice and Sharp.
It's FREE so, enjoy everyone and happy new year.
1. Using the WinPad (Android) browser, download the following file
http://bit.ly/1YV3pM0
2. Install the app accordingly
3. Configure the app so that it start automatically every time you start you WinPad in Android.
4. you can capture any screen from android using the combination following combination keys:
[Power]+[Volume Down] for 2 seconds.
Sample screen captured / print screen. Nice and Sharp.
It's FREE so, enjoy everyone and happy new year.
Monday, November 16, 2015
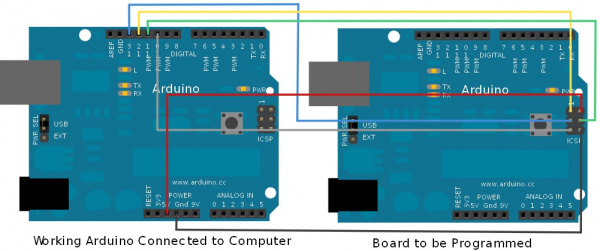
Playing around with Arduino UNO R3 clone from China
First of all, setting up the environment :
1. Download and install the USB-Serial Driver. Saw from the chip surface, mine is using a "WCH CH340G", therefore, need to download the drive and setup separately :
Driver for Arduino Clone with WCH CH340G
2. Setup and configure Arduino IDE
- Run into problem while running the Zip version of the IDE at first. Now, it run well after configured the "sketchpath" in "preferences.txt" located in the "lib" folder
After everything is set, and when i plug in the board, all i found is that i can compiled and verified my "Hello World" sketch successfully, but, the upload is unsuccessful. After a few digging, finally found the solution for it :
- Luckily, i have a friend with a working UNO R3. Therefore i am using his Arduino UNO R3 as ISP.
- First i open the example sketch "ArduinoISP" provided inside the IDE.
- Upload the sketch into my friend's working board.
- I connect my board as following :
- Select "Arduino as ISP" as programmer
- Select the serial port for the working Arduino
- Press "Burn Bootloader"
Magic Happen... it seem like my cheap Arduino UNO R3 i bought from Aliexpress is not loaded with bootloader. And now, it's work flawlessly.
.
Tuesday, May 05, 2015
View your Android Screen remotely in you PC without additional devices.
This is one of the way i found out to view screen of my Android device in my Windows PC wireless-ly and FREE-ly without any additional device. I found that it's useful when i am presenting some android app and feature during the presentation. and further more it's FREE and only with few lines of command. And here is it :
1. download and extract a java app from the following URL :
http://droid-at-screen.ribomation.com/download/
2. To run the app, you need to have java run time configured which i am going to discuss here.
3. Run the java app above and connect your android device via a USB cable. you should be able to see your android screen in your pc. However to make it run wireless, follow the following steps.
4. You need to find out what the ip address that's assigned to your android device. Under your command prompt, run "./adb shell" follow by "netcfg" and quite the adb shell by issueing "exit"
5. Then issue the command "adb tcpip 5555"
6. follow by "adb connect [device ip]:5555"
7. There you are, you are now able to disconnect the USB and start to view your android device screen without wire.
Hope you enjoy this FREE thing.
Monday, March 16, 2015
Android Debugging Without Wire / Using WIFI
Recently i have involved in developing android app. Debugging using a device with USB connection has been a disaster for me as i have a loosen USB cable. Therefore have do some finding and here the solution to debug android app without using the USB Cable :
1.First connect your device via USB and make sure debugging is working fine.
2.Second you need to find out what the ip address that's assigned to your android device. Under your command prompt, run "./adb shell" follow by "netcfg" and quite the adb shell by issueing "exit"
3. Then issue the command "adb tcpip 5555"
4. follow by "adb connect [device ip]:5555"
5. There you are, you are now able to disconnect the USB and start to debugging with wire.
To switch back when done , issue the following :
"adb -s [device ip]:5555 usb"
Wednesday, March 11, 2015
Useful FREE graphic tools for android development
Involved in some android app development recently. To make an app interesting, no doubt the image and graphics play a very important. As i am not a full time mobile app developer, nor a graphics designer, i prefer to search for some FREE tools that available to make my life easier while developing mobile application. Following are some of the FREE tool that i come across. Feel free to comment and recommend other tools that you find it useful.
Fotoflexer
Online-Image-Editor
Edit Photo For Free
And again, like always it's FREE... :>
Fotoflexer
Online-Image-Editor
Edit Photo For Free
And again, like always it's FREE... :>
Monday, October 13, 2014
Some OpenSSL Command for my own references maybe it's for you too
General OpenSSL Commands
These commands allow you to generate CSRs, Certificates, Private Keys and do other miscellaneous tasks.
- Generate a new private key and Certificate Signing Request
openssl req -out CSR.csr -new -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -keyout privateKey.key
- Generate a self-signed certificate (see How to Create and Install an Apache Self Signed Certificate for more info)
openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout privateKey.key -out certificate.crt
- Generate a certificate signing request (CSR) for an existing private key
openssl req -out CSR.csr -key privateKey.key -new
- Generate a certificate signing request based on an existing certificate
openssl x509 -x509toreq -in certificate.crt -out CSR.csr -signkey privateKey.key
- Remove a passphrase from a private key
openssl rsa -in privateKey.pem -out newPrivateKey.pem
Checking Using OpenSSL
If you need to check the information within a Certificate, CSR or Private Key, use these commands. You can also check CSRs and check certificates using our online tools.
- Check a Certificate Signing Request (CSR)
openssl req -text -noout -verify -in CSR.csr
- Check a private key
openssl rsa -in privateKey.key -check
- Check a certificate
openssl x509 -in certificate.crt -text -noout
- Check a PKCS#12 file (.pfx or .p12)
openssl pkcs12 -info -in keyStore.p12
Debugging Using OpenSSL
If you are receiving an error that the private doesn't match the certificate or that a certificate that you installed to a site is not trusted, try one of these commands. If you are trying to verify that an SSL certificate is installed correctly, be sure to check out the SSL Checker.
- Check an MD5 hash of the public key to ensure that it matches with what is in a CSR or private key
openssl x509 -noout -modulus -in certificate.crt | openssl md5 openssl rsa -noout -modulus -in privateKey.key | openssl md5 openssl req -noout -modulus -in CSR.csr | openssl md5
- Check an SSL connection. All the certificates (including Intermediates) should be displayed
openssl s_client -connect www.paypal.com:443
Converting Using OpenSSL
These commands allow you to convert certificates and keys to different formats to make them compatible with specific types of servers or software. For example, you can convert a normal PEM file that would work with Apache to a PFX (PKCS#12) file and use it with Tomcat or IIS. Use our SSL Converter to convert certificates without messing with OpenSSL.
- Convert a DER file (.crt .cer .der) to PEM
openssl x509 -inform der -in certificate.cer -out certificate.pem
- Convert a PEM file to DER
openssl x509 -outform der -in certificate.pem -out certificate.der
- Convert a PKCS#12 file (.pfx .p12) containing a private key and certificates to PEM
openssl pkcs12 -in keyStore.pfx -out keyStore.pem -nodes
You can add -nocerts to only output the private key or add -nokeys to only output the certificates. - Convert a PEM certificate file and a private key to PKCS#12 (.pfx .p12)
openssl pkcs12 -export -out certificate.pfx -inkey privateKey.key -in certificate.crt -certfile CACert.crt
Thursday, February 13, 2014
flappybird source code tutorial
Flappy bird become very famous nowadays. And there are rumors saying that the developer of the game if earning USD50,000 a days for the in app ads. Downloaded it, play few rounds, and i have a feeling that developing such a games shall be pretty easy. Therefore, after some search, finally got a very nice tutorial on how to create flappy bird (clone). Source code and tutorial are provided some more. And like usual, it FREE!!! Follow the link below :
FlappyBird (Clone) Source Code and Tutorial
FlappyBird (Clone) Source Code and Tutorial
Wednesday, December 04, 2013
Are your site blacklisted?
Most of the people involve in Internet Marketing or writing blog know how important is it to get listed or indexed by search engine. Search engine traffic can be an important source of traffic. However, sometimes, due to some issue, you found that it hard to get traffic from this kind of resource. First thing you need to check, is whether you site has been blacklisted. Following are some of the FREE tools for you to check if your site has been blacklisted. Check it out, it's again FREE :
Wednesday, November 27, 2013
PKI Related Standards
Involve in some PKI related project recently and found a interesting resources to get all the PKI related Standards. For my own record purpose, and to help out those that needed, following are the link :
http://www.oasis-pki.org/resources/techstandards/#majorrfcs
In case the above site is not accessiable, following are some of the details:
http://www.oasis-pki.org/resources/techstandards/#majorrfcs
In case the above site is not accessiable, following are some of the details:
|







.jpg)
